✨ Gorgeous Game Instance (Blueprint & C++)
Short Description
The UGorgeousGameInstance class extends the standard Unreal Engine UGameInstance by adding an object variable system, allowing you to store and manage persistent data across level transitions and game sessions.
Long Description
UGorgeousGameInstance enhances the standard Unreal Engine UGameInstance by integrating with the Gorgeous Things object variable system. It provides a structured way to store and access persistent data through the AdditionalGorgeousData property, which is a map of named object variables. This allows you to maintain game state, settings, and other important data that needs to persist across level transitions or be globally accessible throughout your game.
🚀 Features
AdditionalGorgeousData
A map of object variables that extends the standard game instance with persistent data storage capabilities. This property allows you to store various types of data that need to persist across level transitions or be accessible throughout the game.
| Property | Type | Description |
|---|---|---|
AdditionalGorgeousData |
TMap<FName, UGorgeousObjectVariable*> |
A map of named object variables that store additional data for the game instance. |
Tip
You can use this property to store various types of data, such as: - Cached save game data - Current game settings - Player preferences - Global game state information - Any other data that needs to persist across level transitions
Important
Each entry in the map is associated with a unique name and is represented by an UGorgeousObjectVariable. When new entries are added in the editor, their UniqueIdentifier is automatically updated.
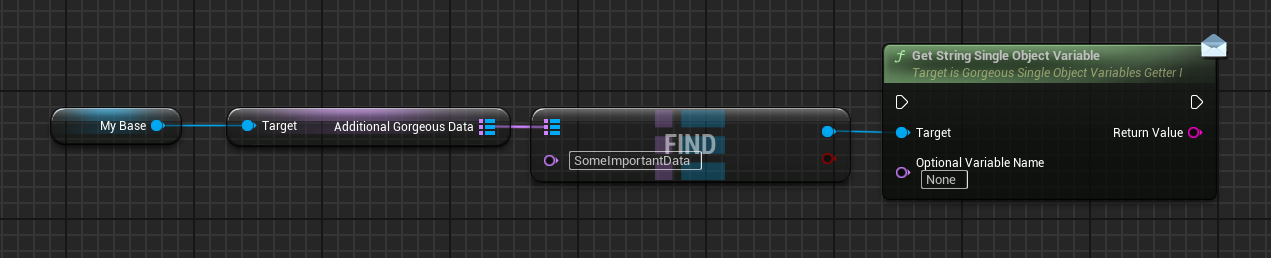
// Accessing data from the AdditionalGorgeousData map
UGorgeousGameInstance* GameInstance = Cast<UGorgeousGameInstance>(GetWorld()->GetGameInstance());
if (GameInstance)
{
// Get a specific object variable by name
UGorgeousObjectVariable* MyData = GameInstance->AdditionalGorgeousData.FindRef(FName("MyDataName"));
if (MyData)
{
// Use the object variable
// ...
}
}
🔧 Implementation Details
The UGorgeousGameInstance class uses several helper macros to simplify its implementation:
UE_DECLARE_QOF_CLASS_INIT_INVOKE_ADDITIONAL_DATA: Used in theInitfunction to initialize the additional data.UE_DECLARE_QOF_CLASS_POST_EDIT_CHANGE_PROPERTY: Used to handle property changes in the editor.
These macros are defined in the GorgeousQualityOfLIfeHelperMacros.h file and provide a standardized way to implement common functionality across different classes in the Gorgeous Things ecosystem.
🔄 Integration with Object Variables
The UGorgeousGameInstance class integrates with the Gorgeous Things object variable system, allowing you to store and manage persistent data. This integration provides several benefits:
- Persistence: Data stored in object variables persists across level transitions and game sessions.
- Type Safety: Object variables provide type safety and validation for stored data.
- Serialization: Object variables can be easily serialized for saving and loading.
- Network Replication: Object variables support network replication for multiplayer games.
To use this functionality, you need to:
- Create a custom game instance class that inherits from
UGorgeousGameInstance. - Add object variables to the
AdditionalGorgeousDatamap in the editor or at runtime. - Access the object variables through the map using their names.